Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) – sometimes also referred to as “nifties” – are unique tokens that can not be interchanged or broken down into smaller parts (as opposed to fungible tokens).
NFTs are unique in their nature, which means there might be only one of them, the original one; they represent a unique asset on a blockchain.
Still confused? Let’s think about it this way: you have a $1 dollar bill, which is worth the same one dollar no matter where you go, and you can replace it with another $1 bill, which indicates that it’s fungible.
But when you have a rare basketball card, you can just replace it with another one because it’s unique and, in the true sense of the word, irreplaceable. And this is what non-fungible means.
Where can NFTs be used?
Based on their unique nature, non-fungible tokens have found their biggest use cases in
- Art
- Images, photos, graphic design, 3D imagery, video
- Music
- Gaming
- Digital collectibles
- Ownership proof
When were they invented?
The initial concept of NFTs appeared in 2012 and was called “colored coins.” It described methods to manage assets on the Bitcoin blockchain. But the idea of the NFTs we know and use today was given birth, metaphorically speaking, in 2017, when a project called CryptoPunks experimented with unique characters on Ethereum.
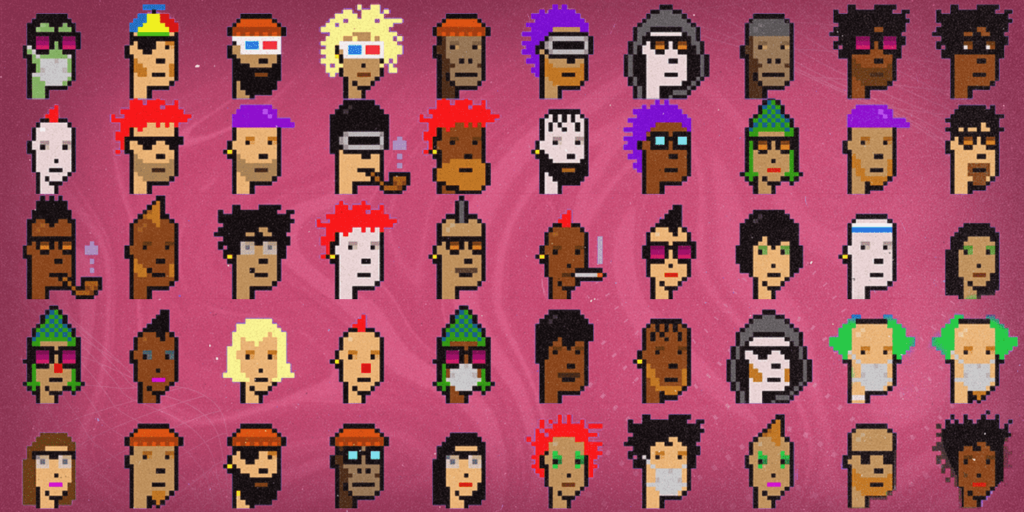

Image: Courtesy of CryptoPunks
To show how the interest in digital collectibles has changed with time, think about the fact that when they were created, Cryptopunks could have been claimed for free by anyone with an Ethereum wallet, and today, the most expensive Crypto Punk, CryptoPunk #5822, costs $23.7 million.
How are NFTs created?
The most popular blockchains used to mint NFTs are Ethereum, Solana, Polygon and Binance Smart Chain, with Ethereum currently leading the way.
When it comes to technical standards NFTs are built on, ERC tends to be the most popular one at the moment. ERC stands for “Ethereum Request for Comment,” one of the most commonly used being ERC20. ERC20 is said to be helpful for developers to create tokens that would need to interact with other tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. But when it comes to gas fees and the speed of the network, this standard is not perfect, and that’s why ERC721 was developed to better serve the needs of non-fungible tokens.
Stay tuned to learn more about NFTs, Crypto and Web3!